Understanding ML to Units Conversion for Tirzepatide & Water-Based Compounds
Mastering ml to units conversion is essential for accurate dosing of water-based compounds like tirzepatide when using U-100 insulin syringes. This guide explains conversions, mixing lyophilized vials, and safe subcutaneous (subQ) injection technique into the belly. At IncreaseMyT, we provide high-quality compounded water-based solutions. Here’s your complete guide to understanding units, preparing your medication, and injecting tirzepatide or similar peptides safely and effectively.
Important Clarification: Insulin Units vs. International Units (IU)
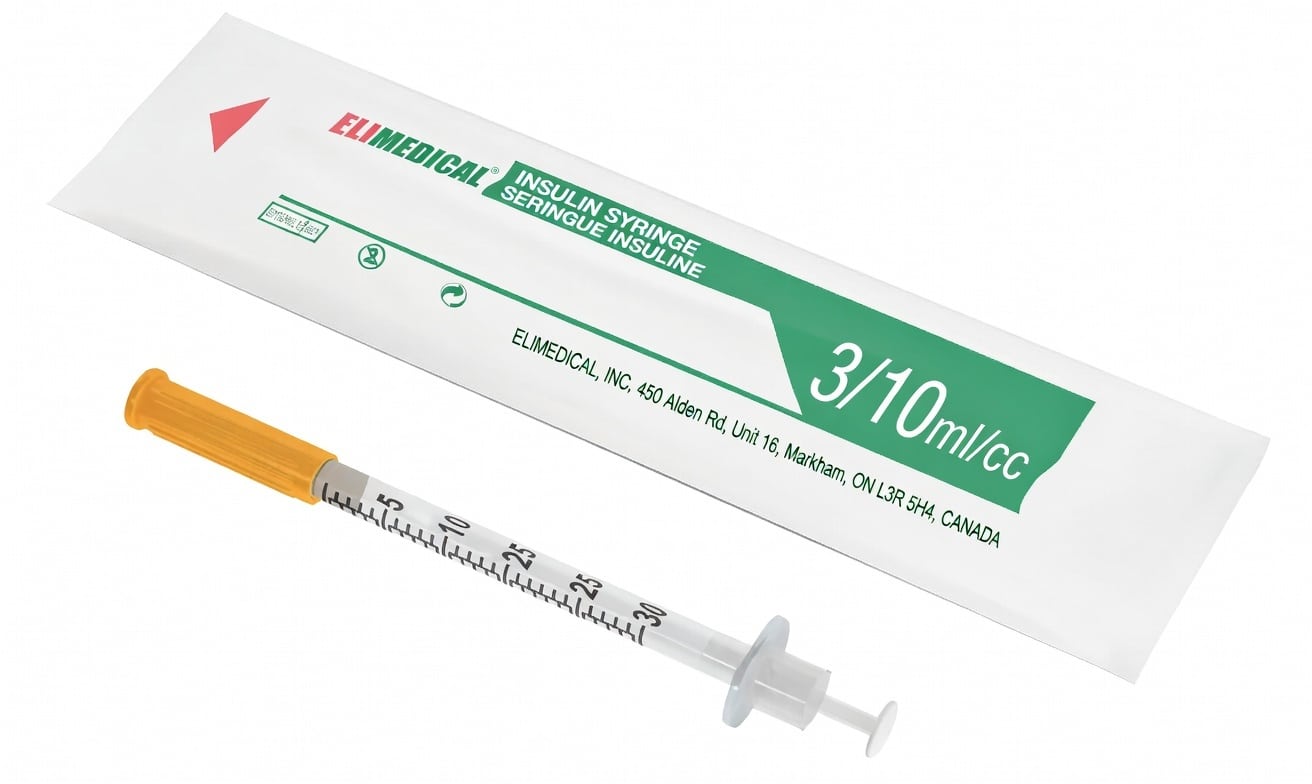
The syringes discussed here are standard U-100 insulin syringes, easily identified by their orange cap (or orange plunger seal). These are marked in “insulin units” where 1 ml always equals 100 units on the U-100 scale—no matter if it's a 0.3 ml, 0.5 ml, or 1 ml syringe. These “units” are not the same as International Units (IU), a separate measurement used for some hormones, vitamins, or biologics. Always confirm you’re using the correct U-100 scale and double-check your vial label.
ML to Units Conversion: Why Concentration Matters
Water-based compounds like tirzepatide come in different concentrations (expressed as mg of active ingredient per ml of solution). Because all U-100 syringes treat 1 ml as 100 units, the amount of mg you get per unit depends entirely on the vial's concentration.
Key note on tirzepatide concentrations:
Compounded tirzepatide is not standardized—different pharmacies or batches can have different strengths, such as 10 mg/ml, 15 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml, or others. This is critical: Do not assume the same number of units will give you the same mg dose when switching to a new vial. You must always check the exact mg/ml listed on your current vial label and recalculate your units based on that specific concentration.
Here are clear examples using the standard 1 ml = 100 units scale:
If your vial is 15 mg/ml (a common concentration):
- 1 ml = 100 units = 15 mg total
- Each unit delivers 0.15 mg (15 mg ÷ 100 units)
- 10 units = 1.5 mg
- 20 units = 3 mg
- 30 units = 4.5 mg
If your vial is 10 mg/ml:
- Each unit delivers 0.1 mg (10 mg ÷ 100 units)
- 20 units = 2 mg (not 3 mg like in the 15 mg/ml example!)
If your vial is 20 mg/ml:
- Each unit delivers 0.2 mg (20 mg ÷ 100 units)
- 20 units = 4 mg
An easy way to think about it:
Since 1 ml = 100 units on a U-100 syringe, 10 units is exactly 1/10th of a ml (0.1 ml). So, if your vial concentration is 15 mg/ml:
- A full 1 ml contains 15 mg
- Therefore, 1/10th of a ml (10 units) contains 1/10th of 15 mg = 1.5 mg
This quick mental shortcut works for any concentration: Just take the mg/ml number, divide by 10, and that’s how many mg you get in every 10 units.
Examples:
- 15 mg/ml → 10 units = 1.5 mg
- 10 mg/ml → 10 units = 1 mg
- 20 mg/ml → 10 units = 2 mg
Use this simple rule of thumb to double-check your dosing quickly before drawing up your injection. Always verify the concentration printed on your vial every time you start a new one, and use a simple calculator (mg/ml ÷ 100 = mg per unit) to determine your exact dose in units. This prevents accidental under- or overdosing.
Preparing Your Medication: Mixing Lyophilized Vials
Many water-based compounds arrive as lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder and must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water (BAC water).
Supplies Needed:
- Lyophilized vial
- BAC water vial
- Alcohol swabs
- Sterile syringe (1–3 ml for mixing)
Step-by-Step Mixing:
- Wipe both vial stoppers with alcohol swabs and let air dry.
- Draw the required amount of BAC water (per your provider’s instructions—often 1–2 ml).
- Insert needle at a 45° angle into the medication vial. Let water run gently down the inner wall—avoid disturbing the powder.
- Do not shake, swirl, or drop the vial. The solution mixes on its own in minutes. Gently roll if needed after waiting.
- Store unmixed vials and BAC water in the fridge. Once mixed, refrigerate the vial (discard if cloudy or after ~28 days).
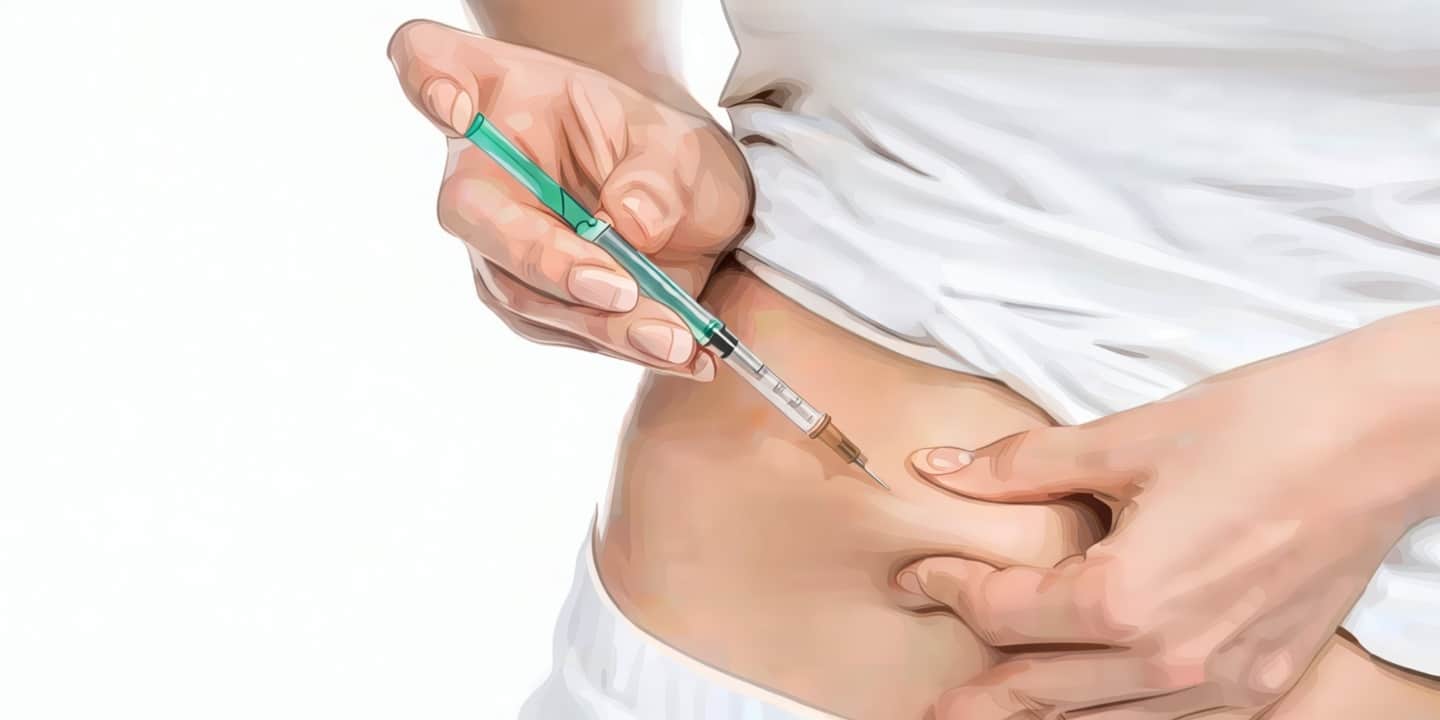
Subcutaneous Injection Guide – Belly (Abdomen)
Water-based compounds absorb well subQ with very low discomfort.
Recommended needle: 31-gauge insulin syringe, 5/16" (8mm) length (0.3 ml / 30-unit size preferred for precision).
Site: Abdomen, 3–4 inches away from the belly button. Rotate sites daily to prevent irritation.
Technique:
- Wash hands thoroughly.
- Swab vial stopper and injection site with alcohol; let air dry.
- Swab injection site with alcohol
- Draw your calculated units (expel air bubbles).
- Pinch or firmly press the skin (optional).
- Insert at 45° angle, inject slowly, hold 5–10 seconds, then withdraw.
- Apply gentle pressure if needed.
Maximum volume per site: 0.5–1 ml (50–100 units) to avoid lumps—though most tirzepatide doses fit easily in a 30-unit syringe.
Never reuse needles. Immediately dispose of used syringes in the sharps container provided. Never place in regular trash—protect sanitation workers from accidental needlesticks.
Storage & Final Tips
Refrigerate all water-based compounds (unmixed and reconstituted) to preserve potency. Avoid freezing.
Never inject if solution is discolored, cloudy, or expired.
Common mistakes: Using old unit amounts with new concentrations, shaking vials, reusing needles, injecting too close to the belly button.
Master these steps for safe, accurate, and comfortable dosing. Contact IncreaseMyT for premium compounded tirzepatide and personalized provider guidance.
Always consult your physician before beginning or changing any therapy. This article is for informational purposes only and not medical advice.